News
Unlocking the Benefits of Phytic Acid: A Comprehensive Guide to This Super Nutrient
Phytic Acid, often regarded as a hidden gem in the realm of nutrition, is gaining recognition for its diverse health benefits. This comprehensive guide aims to illuminate the multifaceted advantages of this super nutrient, which is predominantly found in seeds, grains, and legumes. While traditionally perceived as an anti-nutrient that can inhibit mineral absorption, recent research suggests that Phytic Acid may actually play a vital role in promoting health when consumed as part of a balanced diet.
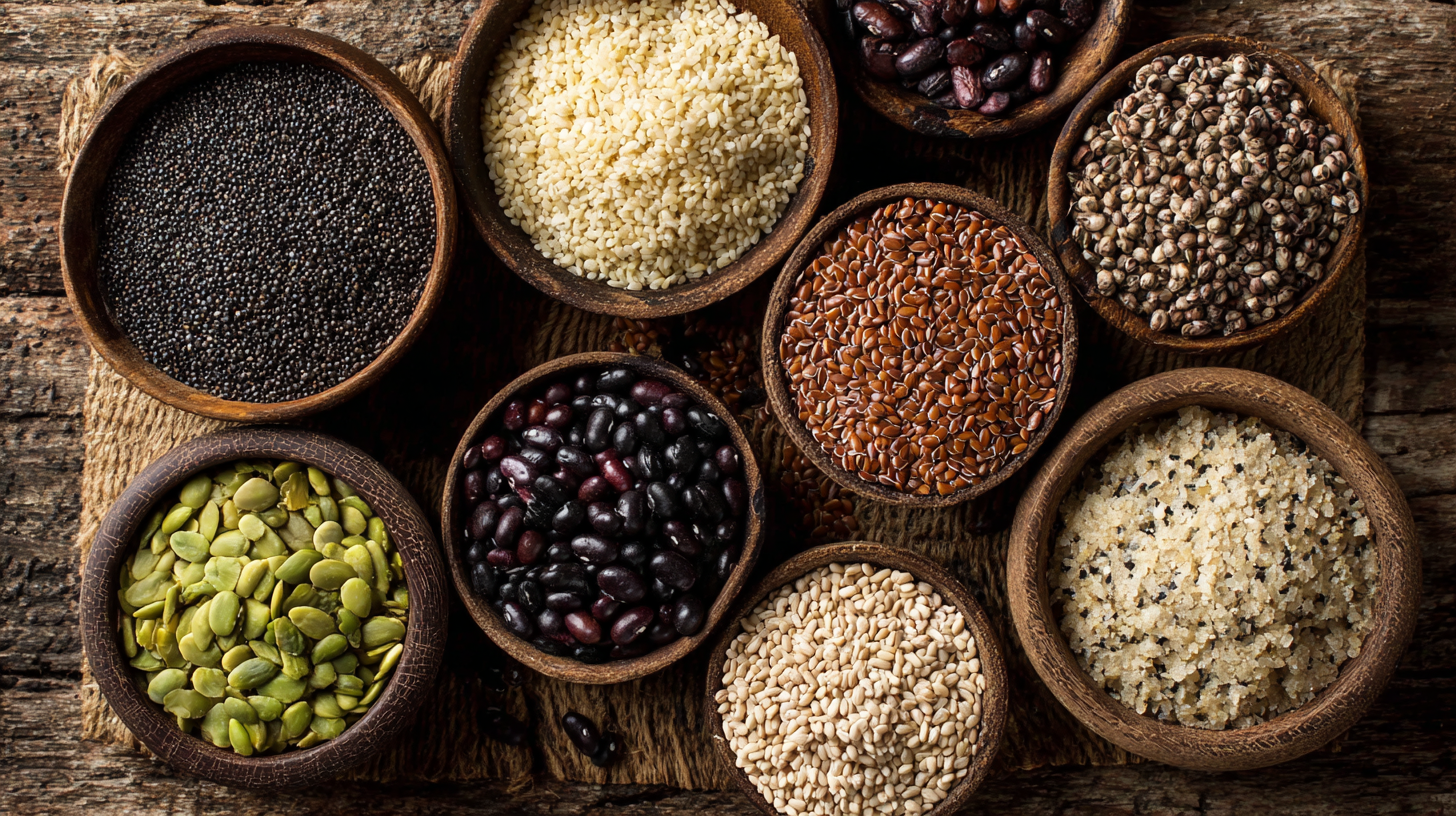

From its potential antioxidant properties to its ability to support digestive health, understanding how to harness the benefits of Phytic Acid can empower individuals to make informed dietary choices. In this guide, we will explore various ways to incorporate this remarkable nutrient into your meals while debunking common misconceptions, ultimately unveiling how Phytic Acid can contribute to a healthier lifestyle.
The Science Behind Phytic Acid: Understanding Its Nutritional Value
Phytic acid, often considered an antinutrient due to its ability to bind minerals and reduce their absorption, deserves a closer examination for its potential health benefits. Found mainly in seeds, grains, and legumes, phytic acid serves as a storage form of phosphorus in plants. Understanding its role in nutrition requires a nuanced perspective, as its effects can vary depending on dietary context and preparation methods.
Research has shown that phytic acid possesses antioxidant properties, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and diabetes. Moreover, it has been linked to improved gut health by promoting the growth of beneficial gut microbiota. Additionally, while phytic acid may inhibit the absorption of certain minerals like iron and zinc, consuming it in conjunction with vitamin C-rich foods can enhance mineral bioavailability. This dual nature of phytic acid positions it not merely as a hindrance but as a valuable component of a balanced diet, encouraging further exploration of its health advantages.
Top 5 Health Benefits of Incorporating Phytic Acid into Your Diet
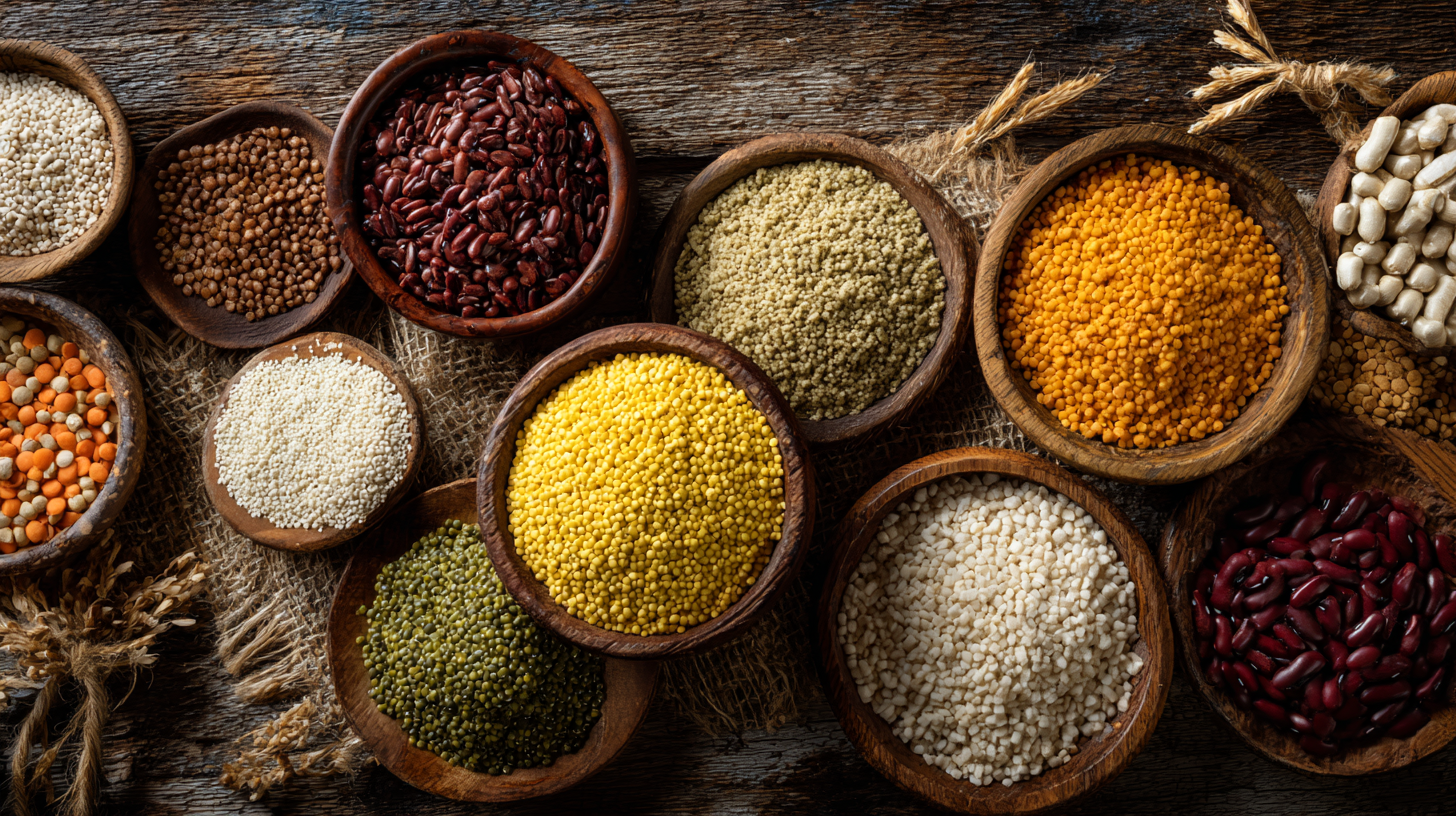 Phytic acid, often dubbed a "super nutrient", is gaining attention for its numerous health benefits. First and foremost, it is known for its powerful antioxidant properties. By neutralizing free radicals, phytic acid helps reduce oxidative stress on the body, potentially lowering the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease. Incorporating foods rich in phytic acid, such as legumes, nuts, and whole grains, into your diet can bolster your overall antioxidant intake.
Phytic acid, often dubbed a "super nutrient", is gaining attention for its numerous health benefits. First and foremost, it is known for its powerful antioxidant properties. By neutralizing free radicals, phytic acid helps reduce oxidative stress on the body, potentially lowering the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease. Incorporating foods rich in phytic acid, such as legumes, nuts, and whole grains, into your diet can bolster your overall antioxidant intake.
Additionally, phytic acid plays a role in enhancing mineral absorption. Although it is often labeled an "anti-nutrient" for binding minerals like iron, calcium, and zinc, evidence suggests that when consumed as part of a balanced diet, it can actually aid in mineral bioavailability over time. This means that incorporating phytic acid-rich foods can support better nutrition, particularly in those with plant-based diets. Furthermore, phytic acid has been linked to improved gut health by promoting beneficial gut bacteria, which is essential for overall digestive wellness.
3 Natural Food Sources Rich in Phytic Acid You Should Try
Phytic acid, often referred to as an "antinutrient," is found predominantly in plant seeds and grains. However, it serves several beneficial roles in nutrition. It can act as a powerful antioxidant, helping to protect cells from oxidative stress, and has been shown to enhance the digestive health by promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. To harness the benefits of phytic acid, incorporating food sources rich in this nutrient is essential.
Three notable foods that are high in phytic acid include whole grains, legumes, and seeds. Whole grains, like oats and brown rice, not only provide phytic acid but also essential vitamins and minerals that support overall health. Legumes, such as lentils and chickpeas, are excellent sources of protein alongside their phytic acid content. Additionally, seeds—particularly pumpkin and sunflower seeds—are packed with nutrients and healthy fats, making them a convenient and healthful option to boost your intake of this super nutrient. Including these foods in your diet can help improve nutrient absorption and contribute to a balanced diet, ultimately enhancing your overall well-being.
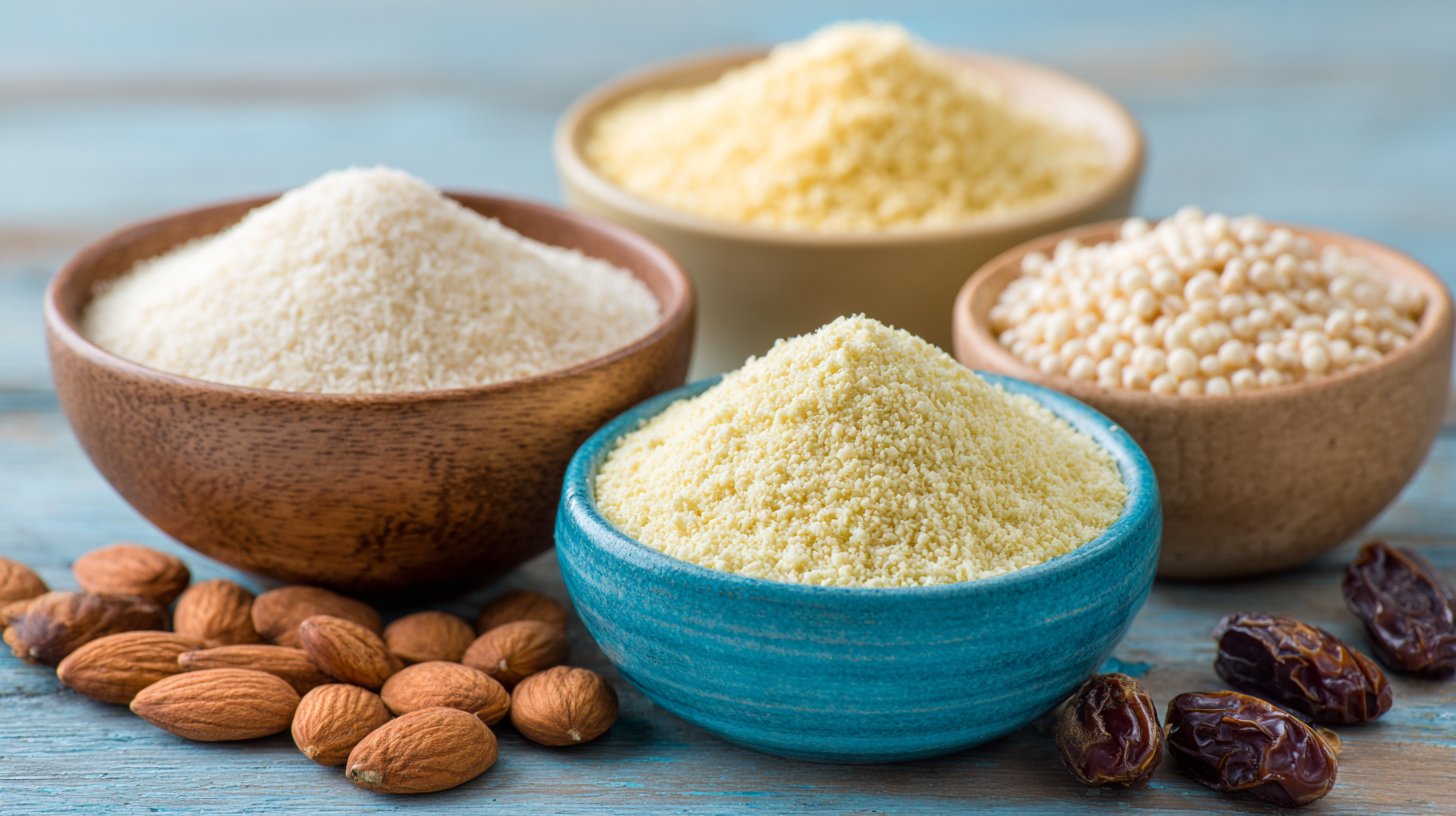

4 Tips for Maximizing Phytic Acid Absorption in Your Meals
Phytic acid, often referred to as a “super nutrient,” is a powerful antioxidant found in many seeds, grains, and nuts. While it boasts several health benefits, the challenge lies in maximizing its absorption during meals. Here are four tips to help you enhance the bioavailability of phytic acid.
Firstly, soaking grains and seeds before cooking can significantly increase phytic acid absorption. This process breaks down the phytic acid and reduces its potential to bind with essential minerals, making them more accessible. Secondly, fermentation is an excellent method to improve nutrient absorption. By allowing grains or legumes to ferment, you activate beneficial enzymes that help digest phytic acid, enhancing its nutritional profile.
Another effective strategy is to combine phytic acid-rich foods with vitamin C sources. Foods high in vitamin C can counteract the inhibitory effects of phytic acid on mineral absorption, promoting a more effective nutrient intake. Lastly, consider adding sprouted grains to your meals. Sprouting not only reduces phytic acid levels but also increases the overall nutrient content of the grains, making them a fantastic addition to your diet. By implementing these tips, you can unlock the full benefits of phytic acid and boost your overall nutrition.
Unlocking the Benefits of Phytic Acid: A Comprehensive Guide to This Super Nutrient - 4 Tips for Maximizing Phytic Acid Absorption in Your Meals
| Food Source | Phytic Acid Content (mg per 100g) | Tips for Maximizing Absorption |
|---|---|---|
| Brown Rice | 950 | Soak before cooking |
| Oats | 390 | Ferment or sprout |
| Legumes (e.g., Lentils) | 2800 | Cook thoroughly |
| Nuts (e.g., Almonds) | 590 | Soak & dry before eating |
Potential Risks: 2 Downsides of Excessive Phytic Acid Intake to Consider
Excessive intake of phytic acid, often found in whole grains, legumes, and nuts, can pose potential risks that should not be overlooked. One primary concern is its impact on mineral absorption. Phytic acid acts as an anti-nutrient by binding to essential minerals such as calcium, magnesium, iron, and zinc, forming insoluble complexes and reducing their bioavailability. According to a study published in the Journal of Nutrition, high levels of phytic acid can lead to deficiencies over time, particularly in diets that rely heavily on these foods without adequate supplementation or diversity.
Another significant downside of excessive phytic acid consumption is its potential contribution to digestive discomfort. Increased intake may lead to gastrointestinal issues, including bloating and gas, as noted in various nutritional studies. This is similar to findings related to high fiber foods, where sudden increases in fiber can overwhelm the digestive system, particularly in individuals unaccustomed to large amounts. Furthermore, while phytic acid offers antioxidant properties, moderation is key to enjoying its benefits while minimizing adverse effects. Balancing phytic acid-rich foods with those high in minerals and fiber can promote optimal health without the associated risks.
Unlocking the Benefits of Phytic Acid
Related Posts
-

Manufactured in China Quality Enhancements of Best Lauryl Azone for Global Markets
-

Understanding Tylosin Phosphate: Revolutionizing Antibiotic Use in Livestock Health
-

Solutions for Enhanced Patient Outcomes: The Role of Ceftriaxone Sodium in Modern Antibiotic Therapy
-

Unlocking the Secrets to Sourcing Valganciclovir Hcl for Your Global Procurement Needs
-

Mastering the Essentials of Best Tylosin Phosphate for Global Procurement Success
-

7 Essential Tips for Effectively Using Bendazole Hcl in Your Business Operations