News
How to Use Ceftriaxone Sodium for Effective Infection Treatment
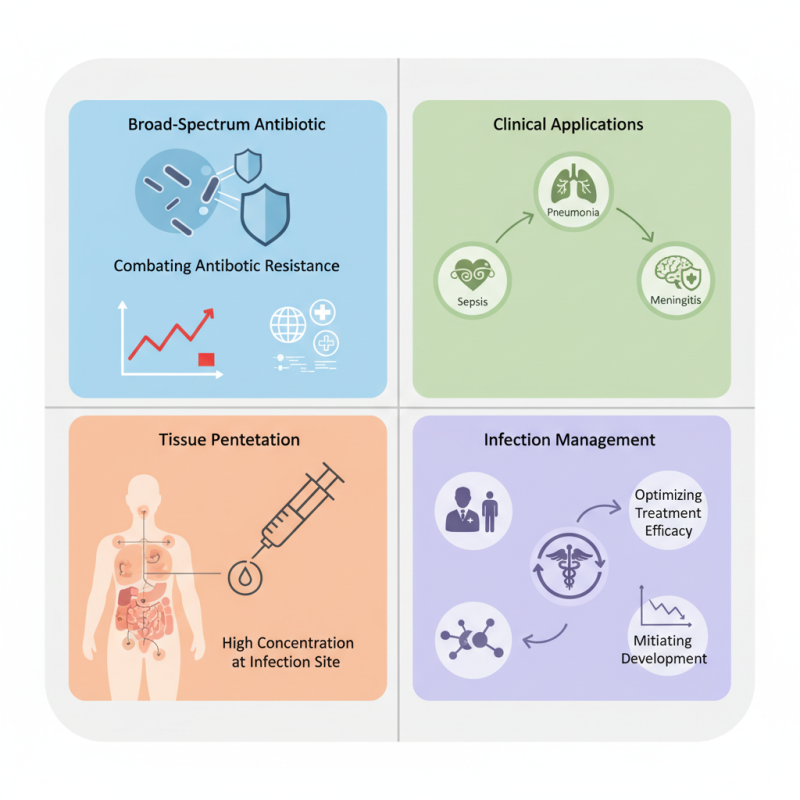
Ceftriaxone Sodium is a broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic that plays a crucial role in the treatment of various bacterial infections. As reported by the World Health Organization (WHO), antibiotic resistance has become a pressing global health concern, with an estimated 700,000 deaths annually attributed to drug-resistant infections. In this context, Ceftriaxone Sodium stands out for its efficacy in managing complicated infections, particularly those caused by gram-negative bacteria. This is supported by data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), which indicate that Ceftriaxone is effective against strains of bacteria that are increasingly resistant to other antibiotics.
The use of Ceftriaxone Sodium has been further reinforced by clinical guidelines, which suggest its application in a range of infections, including pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis. According to a recent study published in the Journal of Clinical Microbiology, regimens that include Ceftriaxone have significantly improved patient outcomes in severe infections. This antibiotic's ability to penetrate various body tissues and achieve high concentrations at the site of infection underlines its importance in contemporary medical practice. As healthcare providers navigate the complexities of infection management, understanding the appropriate use of Ceftriaxone Sodium is essential for optimizing treatment efficacy while mitigating resistance development.
Overview of Ceftriaxone Sodium and Its Uses in Infection Treatment
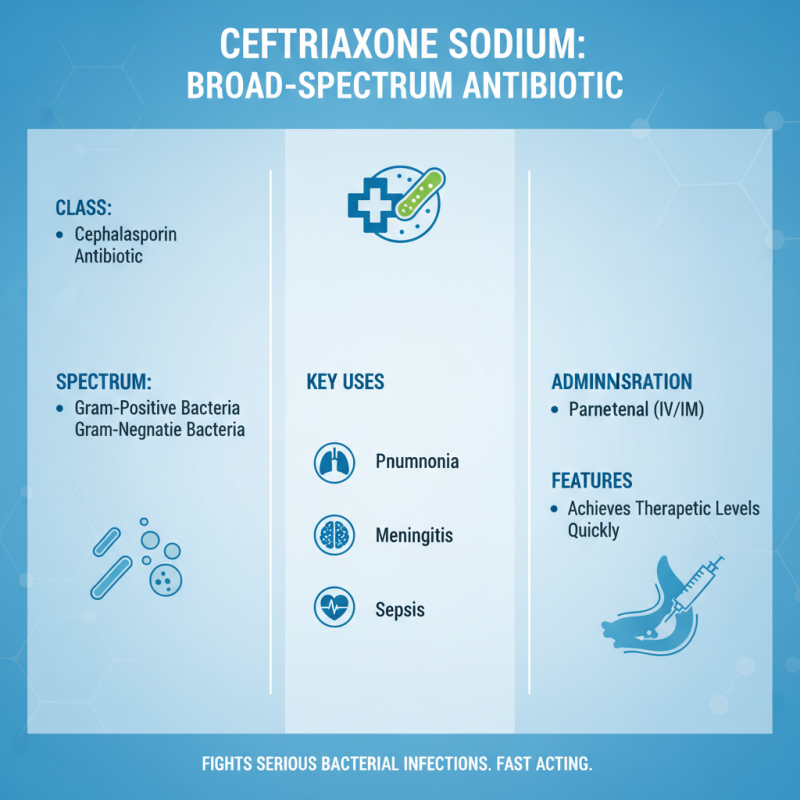
Ceftriaxone sodium is a broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic widely used in the treatment of various bacterial infections. It exhibits a high level of efficacy against a range of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, making it a critical option in managing conditions such as pneumonia, meningitis, and sepsis. Administered parenterally, ceftriaxone allows for rapid absorption and distribution throughout the body, ensuring that therapeutic levels are achieved quickly in infected tissues. This feature is particularly important in serious infections where immediate action is necessary to reduce morbidity and mortality.
The mechanism of action of ceftriaxone involves inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, which is crucial for bacterial growth and replication. By disrupting this process, ceftriaxone causes the bacteria to lose structural integrity, leading to cell lysis and death. Its extended half-life allows for once or twice daily dosing, enhancing patient compliance and facilitating smoother treatment regimens. Ceftriaxone is often preferred in hospital settings due to its potency and versatility, as it can be utilized in combination with other antibiotics to target polymicrobial infections effectively, further expanding its clinical applicability in infection treatment.
Mechanism of Action: How Ceftriaxone Sodium Works Against Bacterial Infections
Ceftriaxone sodium is a broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic commonly used in the treatment of various bacterial infections. Its mechanism of action centers around inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. Ceftriaxone binds to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located in the bacterial cell membrane, which play a crucial role in the final stages of cell wall production. This binding disrupts the cross-linking of peptidoglycan chains, leading to a weakened cell wall structure and ultimately causing cell lysis and death.
Furthermore, ceftriaxone demonstrates effectiveness against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria by virtue of its ability to penetrate the outer membrane of Gram-negative organisms. The antibiotic's stability against certain beta-lactamases enhances its efficacy by allowing it to remain active in the presence of enzymes that would normally inactivate other penicillins. This dual mechanism not only broadens its spectrum of activity but also ensures that it can target resistant strains, making it a valuable option in managing severe or complicated infections.
How to Use Ceftriaxone Sodium for Effective Infection Treatment
| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ceftriaxone Sodium |
| Drug Class | Third-Generation Cephalosporin |
| Mechanism of Action | Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis |
| Indications | Bacterial infections, including pneumonia, meningitis, and urinary tract infections |
| Route of Administration | Intravenous or intramuscular injection |
| Dosage | Typically 1-2 g once daily, depending on the infection |
| Side Effects | Diarrhea, rash, allergic reactions, potential for Clostridium difficile infection |
| Contraindications | Hypersensitivity to cephalosporins, severe renal impairment |
| Storage | Store in a cool, dry place away from light |
Dosage Guidelines for Adult and Pediatric Patients on Ceftriaxone Sodium
Ceftriaxone sodium is a broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic commonly used to treat a variety of infections. Proper dosage is crucial for ensuring both efficacy and safety, and it varies significantly between adult and pediatric patients. For adults, the usual dosage ranges from 1 to 2 grams administered intravenously or intramuscularly once daily, depending on the severity of the infection and the patient's specific health condition. In cases of severe infections, such as pneumonia or sepsis, higher doses may be warranted, but careful monitoring of renal function is advisable due to the potential for toxicity.
In pediatric patients, the dosage of ceftriaxone is typically calculated based on body weight, with the standard recommendation being 50 to 75 milligrams per kilogram of body weight, given once daily. For certain serious infections, such as septicemia or meningitis, dosages may increase to a maximum of 100 milligrams per kilogram. It is important to note that ceftriaxone should not be administered concurrently with calcium-containing solutions in pediatric patients due to the risk of precipitation. Therefore, clinicians must tailor the dosage, considering both the age and weight of the patient, as well as the specific type of infection being treated, to optimize therapeutic outcomes while minimizing risks.
Usage of Ceftriaxone Sodium in Infection Treatment
Potential Side Effects and Contraindications of Ceftriaxone Sodium
Ceftriaxone sodium is a broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic widely utilized for treating various bacterial infections. However, like all medications, it carries potential side effects and contraindications that practitioners must consider. Notably, one concerning side effect is the increased risk of hypersensitivity reactions, which can manifest as skin rashes, itching, or severe anaphylactic responses in susceptible individuals. According to the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, approximately 1 to 3% of patients receiving beta-lactam antibiotics, including cephalosporins like ceftriaxone, display such allergic reactions.
Another significant risk associated with ceftriaxone sodium is its interaction with certain medications and its contraindication in patients with specific medical conditions. Patients with a history of jaundice associated with ceftriaxone or those who are receiving calcium supplements should be closely monitored, as concurrent administration can lead to serious complications such as precipitation in the lungs and kidneys. Data from a study published in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy highlights that ceftriaxone should be avoided in neonates due to the potential for bilirubin displacement and subsequent kernicterus, presenting an important consideration in pediatrics.
Thus, while ceftriaxone remains a critical tool in combating infections, understanding its potential side effects and contraindications is essential for safe and effective use in clinical practice.
Best Practices for Monitoring Patients During Ceftriaxone Treatment

Monitoring patients during ceftriaxone treatment is crucial to ensure both effectiveness and safety. Healthcare professionals should start by assessing the patient's renal function before initiating therapy, as ceftriaxone is primarily eliminated through the kidneys. Regularly checking serum creatinine levels and monitoring for any signs of renal impairment during the course of treatment can help prevent potential complications. Additionally, it is important to observe patients for any allergic reactions or side effects, such as gastrointestinal disturbances or signs of superinfection, which may indicate the need for treatment adjustments.
Moreover, maintaining regular communication with the patient can enhance monitoring efforts. Educating patients about the importance of reporting any unusual symptoms, such as rash, fever, or changes in urine output, empowers them to participate in their treatment plan actively. Clinicians should encourage follow-up visits or phone consultations to reassess treatment efficacy and adjust the therapy as needed. Close monitoring not only fosters a better therapeutic outcome but also minimizes adverse effects, ultimately leading to a safer and more effective treatment experience for patients receiving ceftriaxone.
Related Posts
-

Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding and Using Best Ceftriaxone Sodium Effectively
-

Solutions for Enhanced Patient Outcomes: The Role of Ceftriaxone Sodium in Modern Antibiotic Therapy
-

The Essential Role of Ceftriaxone Sodium in Modern Antibiotic Therapy: What You Need to Know
-

Understanding the Role of Ceftriaxone Sodium in Modern Antibiotic Treatments
-

How Chinese Manufacturers Thrive Amid US China Tariff Challenges with Best Ceftriaxone Sodium
-

Solutions for Enhancing Global Procurement of Best Valaciclovir Hcl with Unmatched Quality Assurance